5. Model Conversion Advanced Guide
5.1. Pulsar Build model compilation
This section describes the complete use of the pulsar build command.
5.1.1. Overview
pulsar build is used for model optimization, quantization, compilation, and other operations. A diagram of its operation is shown below:
pulsar build takes the input model (model.onnx) and the configuration file (config.prototxt) and compiles them to get the output model (joint) and the output configuration file (output_config.prototxt).
The command line arguments of pulsar build will override some parts of the configuration file and cause pulsar build to output the overwritten configuration file. See Configuration file details for a detailed description of the configuration file.
pulsar build -h shows detailed command line arguments:
1root@xxx:/data# pulsar build -h
2usage: pulsar build [-h] [--config CONFIG] [--output_config OUTPUT_CONFIG]
3 [--input INPUT [INPUT ...]] [--output OUTPUT [OUTPUT ...]]
4 [--calibration_batch_size CALIBRATION_BATCH_SIZE]
5 [--compile_batch_size COMPILE_BATCH_SIZE [COMPILE_BATCH_SIZE ...]]
6 [--batch_size_option {BSO_AUTO,BSO_STATIC,BSO_DYNAMIC}]
7 [--output_dir OUTPUT_DIR]
8 [--virtual_npu {0,311,312,221,222,111,112}]
9 [--input_tensor_color {auto,rgb,bgr,gray,nv12,nv21}]
10 [--output_tensor_color {auto,rgb,bgr,gray,nv12,nv21}]
11 [--output_tensor_layout {native,nchw,nhwc}]
12 [--color_std {studio,full}]
13 [--target_hardware {AX630,AX620,AX170}]
14 [--enable_progress_bar]
15
16optional arguments:
17 -h, --help show this help msesage and exit
18 --config CONFIG .prototxt
19 --output_config OUTPUT_CONFIG
20 --input INPUT [INPUT ...]
21 --output OUTPUT [OUTPUT ...]
22 --calibration_batch_size CALIBRATION_BATCH_SIZE
23 --compile_batch_size COMPILE_BATCH_SIZE [COMPILE_BATCH_SIZE ...]
24 --batch_size_option {BSO_AUTO,BSO_STATIC,BSO_DYNAMIC}
25 --output_dir OUTPUT_DIR
26 --virtual_npu {0,311,312,221,222,111,112}
27 --input_tensor_color {auto,rgb,bgr,gray,nv12,nv21}
28 --output_tensor_color {auto,rgb,bgr,gray,nv12,nv21}
29 --output_tensor_layout {native,nchw,nhwc}
30 --color_std {studio,full}
31 only support nv12/nv21 now
32 --target_hardware {AX630,AX620,AX170}
33 target hardware to compile
34 --enable_progress_bar
Hint
Complex functions can be implemented using configuration files, and command-line arguments only play a supporting role. In addition, the command line parameters override some of the corresponding configuration in the configuration file.
5.1.2. Detailed explanation of parameters
- pulsar build Parameter explanation
- --input
The input model path for this compilation, corresponding to the input_path field in
config.prototxt- --output
Specify the file name of the output model, e.g.
compiled.joint, corresponding to output_path field inconfig.prototxt- --config
Specifies the basic configuration file used to guide the compilation process. If command-line arguments are specified for the
pulsar buildcommand, the values specified in the command-line arguments will be used in preference to those specified in the conversion model- --output_config
Outputs the complete configuration information used in this build to a file
- --target_hardware
Specify the hardware platform for compiling the output model, currently
AX630andAX620are available- --virtual_npu
Specify the virtual NPU to be used for inference, please differentiate according to the
-target_hardwareparameter. See the virtual NPU section in chip_introduction for details- --output_dir
Specifies the working directory for the compilation process. The default is the current directory
- --calibration_batch_size
The
batch_sizeof the data used for internal parameter calibration in the transcoding process. The default value is32.- --batch_size_option
Sets the
batchtype supported by thejointformat model:BSO_AUTO: default option, static by defaultbatchBSO_STATIC: staticbatch, fixedbatch_sizeduring inference, optimal performanceBSO_DYNAMIC: dynamicbatch, supports arbitrarybatch_sizeup to the maximum value when reasoning, most flexible
- --compile_batch_size
Sets the
batch sizesupported by thejointformat model. The default is1.When
-batch_size_option BSO_STATICis specified,batch_sizeindicates the uniquebatch sizethat thejointformat model can use for reasoning.When
-batch_size_option BSO_DYNAMICis specified,batch_sizeindicates the maximumbatch sizethat can be used forjointformat model inference.
- --input_tensor_color
Specify the color space of input data for input model, optional:
- Default option:
auto, automatic recognition based on the number of input channels to the model 3-channel is
bgr1-channel is
gray
- Default option:
Other options:
rgb,bgr,gray,nv12,nv21
- --output_tensor_color
Specify the color space of the input data for the output model, optional:
- Default option:
auto, automatic recognition based on the number of input channels to the model 3-channel is
bgr1-channel is
gray
- Default option:
Other options:
rgb,bgr,gray,nv12,nv21
- --color_std
Specify the conversion standard to be used when converting between
RGBandYUV, options:legacy,studioandfull, default islegacy- --enable_progress_bar
Show progress bar at compile time. Not shown by default
- --output_tensor_layout
Specify the
layoutof the output model of thetensor, optional:native: default option, legacy option, not recommended. It is recommended to explicitly specify the outputlayoutnchwnhwc
Attention
This parameter is only supported by
axera_neuwizard_v0.6.0.1and later toolchains. Starting fromaxera_neuwizard_v0.6.0.1, the defaultlayoutof the outputtensorof someAX620Amodels may be different from the defaultlayoutof theaxera_neuwizard_v0.6.0.1. may differ from the model compiled from the toolchain of previous versions ofaxera_neuwizard_v0.6.0.1. The defaultlayoutof theAX630Amodel is not affected by the toolchain version
Code examples
1pulsar build --input model.onnx --output compiled.joint --config my_config.prototxt --target_hardware AX620 --virtual_npu 111 --output_config my_output_config.prototxt
Tip
When generating joint models that support dynamic batch, multiple common batch_size can be specified after -compile_batch_size to improve performance when reasoning with batch size up to these values.
Attention
Specifying multiple batch sizes will increase the size of the joint model file.
5.2. Pulsar Run model simulation and alignment
This section describes the complete use of the pulsar run command.
5.2.1. Overview
pulsar run is used to perform x86 simulation and precision pair splitting of joint models on the x86 platform.
pulsar run -h shows detailed command line arguments:
1root@xxx:/data# pulsar run -h
2usage: pulsar run [-h] [--use_onnx_ir] [--input INPUT [INPUT ...]]
3 [--layer LAYER [LAYER ...]] [--output_gt OUTPUT_GT]
4 [--config CONFIG]
5 model [model ...]
6
7positional arguments:
8 model
9
10optional arguments:
11 -h, --help show this help msesage and exit
12 --use_onnx_ir use NeuWizard IR for refernece onnx
13 --input INPUT [INPUT ...] input paths or .json
14 --layer LAYER [LAYER ...] input layer namse
15 --output_gt OUTPUT_GT save gt data in dir
16 --config CONFIG
- pulsar run Parameter explanation
Required parameters
model.jointmodel.onnx- --input
Multiple input data can be specified and used as input data for the simulation
inference. Supportjpg,png,bin, etc., and make sure the number of them is the same as the number of model input layers- --layer
- Not requiredWhen the model has multiple inputs, it is used to specify which layer the input data should be on. The order is in contrast to
-input.For example,-input file1.bin file2.bin --layer layerA layerBmeans inputfile1.bintolayerAand inputfile2.bintolayerB, making sure that the length of-layeris the same as the length of-input. - --use_onnx_ir
- This option tells
pulsar runto internally infer theonnxmodel withNeuWizard IRwhen using theonnxformat model as a counterpoint reference model. By default,NeuWizard IRis not used.This option is only meaningful if `` –onnx`` is specified, it can be ignored - --output_gt
Specifies the directory where the simulation
inferenceresults of the target model and the upper board input data are stored. No output by default- --config
Specifies a configuration file to guide
pulsar runin the internal conversion of the reference model. The configuration file is generally output using the-pulsar build--output_configoption
pulsar run code example
pulsar run model.onnx compiled.joint --input test.jpg --config my_output_config.prototxt --output_gt gt
5.3. Pulsar Info View model information
Attention
Note: The pulsar info feature will only work with docker toolchains with version numbers greater than 0.6.1.2.
For .joint models transferred from an old toolchain, the correct information cannot be seen with pulsar info and needs to be reconverted with a newer toolchain. The reason is that the Performance.txt file in the old joint does not contain the onnx layer name information and needs to be reconverted.
pulsar info is used to view information about onnx and joint models, and supports saving model information to html, grid, jira formats.
Usage commands
pulsar info model.onnx/model.joint
Parameter list
$ pulsar info -h
usage: pulsar info [-h] [--output OUTPUT] [--output_json OUTPUT_JSON]
[--layer_mapping] [--performance] [--part_info]
[--tablefmt TABLEFMT]
model
positional arguments:
model
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help msesage and exit
--output OUTPUT path to output dir
--output_json OUTPUT_JSON
--layer_mapping
--performance
--part_info
--tablefmt TABLEFMT possible formats (html, grid, jira, etc.)
Parameter description
- pulsar info Parameter explanation
- --output
Specify the directory where the model information is saved, not saved by default
- --output_json
Save the full model information as Json, not saved by default
- --layer_mapping
Show layer_mapping information of Joint model, not shown by default
Can be used to see the correspondence between onnx layer and the converted lava layer
- --performance
Show performance information of Joint model, not shown by default
- --parts
Displays all information about each part of the Joint model, not shown by default
- --tablefmt
- Specify the format for displaying and saving model information, optional:
simple: DEFAULT
grid
html
jira
… Any of the tablefmt formats supported by the tabulate library
Example: View basic model information
pulsar info resnet18.joint
# output log
[24 18:40:10 wrapper_pulsar_info.py:32] Information of resnet18.joint:
IO Meta Info:
NAME I/O? SHAPE DTYPE LAYOUT
-------------------- ------ ---------------- ------- --------
data INPUT [1, 224, 224, 3] uint8 NHWC
resnetv15_dense0_fwd OUTPUT [1, 1000] float32 NCHW
Approx System Memory: 13.84 MB
Approx Standard Memory: 0 B
Approx Memory: 13.84 MB
Virtual NPU: AX620_VNPU_111
Static Batch: 1
Toolchain Version: dfdce086b
Example: See the correspondence between the onnx layer and the layer of the compiled model
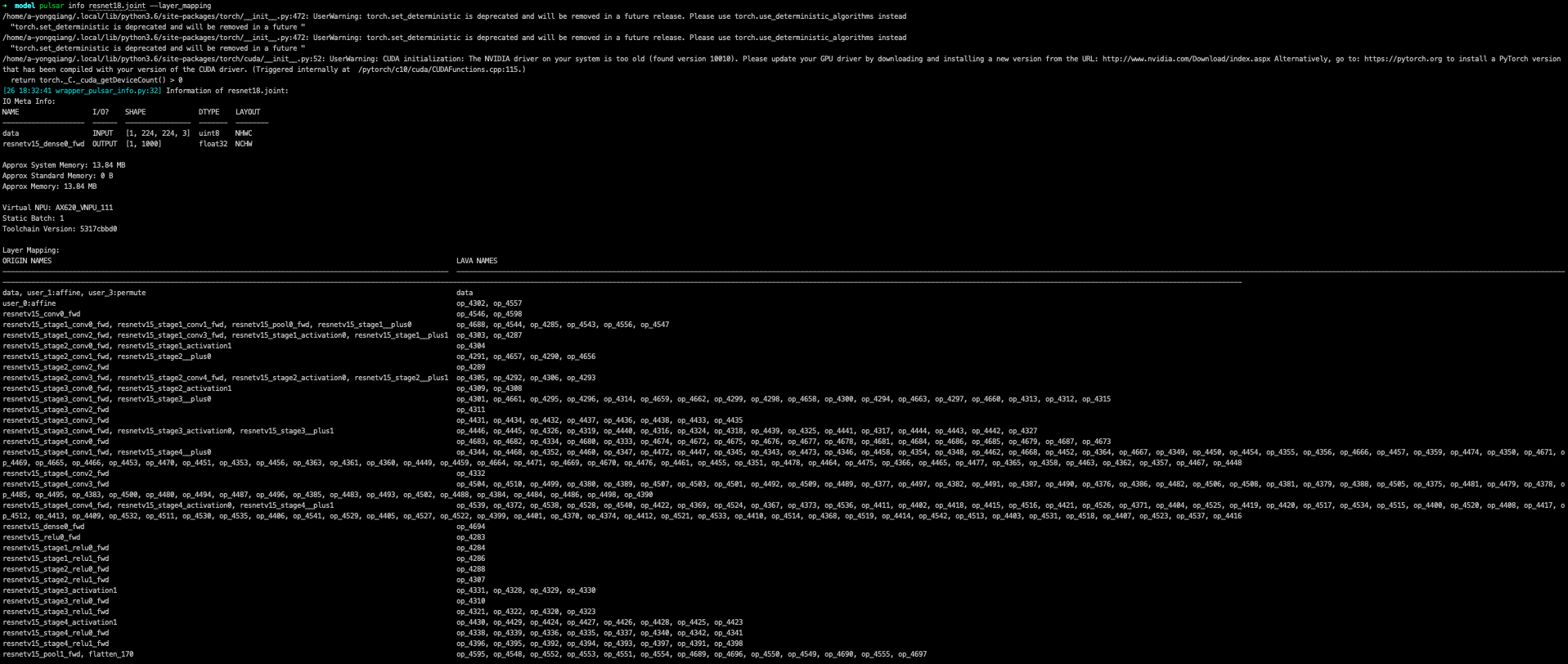
where ORIGIN_NAmse is the layer name of the original onnx, and LAVA_NAmse is the layer name of the compiled model.
Note
Specify the parameters in pulsar info:
--layer_mappingparameter to see the correspondence betweenonnx_layer_nameand thelayer_nameof the transformed modelThe
--performanceparameter allows you to see theperformanceinformation for eachlayer.
5.4. Pulsar Version View Toolchain Version
pulsar version is used to get the tool version information.
Hint
If you need to provide us with toolchain error information, please submit the version of the toolchain you are using along with the information.
Code examples
pulsar version
Example result
0.5.34.2
7ca3b9d5
5.5. Tools
The Pulsar toolchain also provides other common network model processing tools, which help users to format the network model and other functions.
5.5.1. Caffe2ONNX
The dump_onnx.sh tool is pre-installed in the Docker image of Pulsar, providing the ability to convert Caffe models to ONNX models, thus indirectly extending pulsar build support for Caffe models. This is done as follows:
dump_onnx.sh -h to display detailed command line arguments:
1root@xxx:/data$ dump_onnx.sh
2Usage: /root/caffe2onnx/dump_onnx.sh [prototxt] [caffemodel] [onnxfile]
Option explanation
[prototxt]
The path to the
*.prototxtfile of the inputcaffemodel[caffemodel]
The path to the
*.caffemodelfile for the inputcaffemodel[onnxfile]
The output
*.onnxmodel file path
Code examples
1root@xxx:/data$ dump_onnx.sh model/mobilenet.prototxt model/mobilenet.caffemodel model/mobilenet.onnx
A sample log message is as follows
1root@xxx:/data$ dump_onnx.sh model/mobilenet.prototxt model/mobilenet.caffemodel model/mobilenet.onnx
22. start model conversion
3=================================================================
4Converting layer: conv1 | Convolution
5Input: ['data']
6Output: ['conv1']
7=================================================================
8Converting layer: conv1/bn | BatchNorm
9Input: ['conv1']
10Output: ['conv1']
11=================================================================
12Converting layer: conv1/scale | Scale
13Input: ['conv1']
14Output: ['conv1']
15=================================================================
16Converting layer: relu1 | ReLU
17Input: ['conv1']
18Output: ['conv1']
19=================================================================
20####Omitting several lines ############
21=================================================================
22Node: prob
23OP Type: Softmax
24Input: ['fc7']
25Output: ['prob']
26====================================================================
272. onnx model conversion done
284. save onnx model
29model saved as: model/mobilenet.onnx
5.5.2. parse_nw_model
Function
Statistics joint model cmm usage
1usage: parse_nw_model.py [-h] [--model MODEL]
2
3optional arguments:
4 -h, --help show this help msesage and exit
5 --model MODEL dot_neu or joint file
Example of usage
The following commands are only available for the toolchain docker environment
1python3 /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools/parse_nw_model.py --model yolox_l.joint
2python3 /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools/parse_nw_model.py --model part_0.neu
Example of returned results
1{'McodeSize': 90816, 'WeightsNum': 1, 'WeightsSize': 568320, 'ringbuffer_size': 0, 'input_num': 1, 'input_size': 24576, 'output_num': 16, 'output_size': 576}
Field Description
field |
Description |
|---|---|
unit |
Byte |
McodeSize |
Binary Code Size |
WeightsNum |
Indicates the number of weights |
WeightsSize |
Weights Size |
ringbuffer_size |
Indicates the DDR Swap space to be requested during the model run |
input_num |
indicates the number of input Tensors for the model |
input_size |
Input Tensor Size |
output_num |
Number of output Tensor |
output_size |
Output Tensor Size |
Hint
This script counts the CMM memory of all .neu files in the joint model, and returns the sum of the parsed results of all .neu files.
5.5.3. joint model initialization speed patch tool
Overview
Hint
For neuwizard-0.5.29.9 and earlier toolchain conversions of joint model files,
can be refreshed offline using the optimize_joint_init_time.py tool to reduce the joint model load time, with no change in inference results or time.
How to use
cd /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools
python3 optimize_joint_init_time.py --input old.joint --output new.joint
5.5.4. Convert ONNX subplots in joint models to AXEngine subplots
How to use
Hint
The joint model named input.joint (implemented with ONNX as the CPU backend) can be converted to a joint model (implemented with AXEngine as the CPU backend) with the following command, and optimization mode enabled.
python3 /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools/joint_onnx_to_axe.py --input input.joint --output output.joint --optimize_slim_model
Parameter Definition
- Parameter Definition
- --input
Input for the conversion tool
jointmodel path- --output
The output of the conversion tool
jointmodel path- --optimize_slim_model
Turn on the optimization mode. It is recommended when the network output feature map is small, otherwise it is not recommended
5.5.5. wbt_tool Instructions for use
Background
Some models need different network weights for different usage scenarios, for example, the usage scenario of VD model is divided into day and night, both networks have the same structure, but the weights are different, is it possible to set different weights for different scenarios, i.e., the same model keeps multiple sets of weight information
The
wbt_toolscript provided in thePulsartool chainDockercan be used to realize the need for one model with multiple sets of parameters
Tools Overview
Tool path: /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools/wbt_tool.py, note that you need to give wbt_tool.py executable permissions
# Add executable permissions
chmod a+x /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools/wbt_tool.py
- wbt_tool function parameters
- info
View the action to see the
wbtname information for thejointmodel, and if it isNone, you need to specify it manually whenfuse.- fuse
Merge operation to combine multiple
jointmodels with the same network structure and different network weights into onejointmodel with multiple weights- split
split operation, which splits a
jointmodel with multiple weights into multiplejointmodels with the same network structure and different network weights
Use restrictions
Warning
Merging between joint'' models with multiple copies of ``wbt is not supported,
Please split the joint model with single copy of wbt first, and then merge it with other models if needed.
Example 1
View the wbt information of model model.joint:
<wbt_tool> info model.joint
part_0.neu's wbt_namse:
index 0: wbt_#0
index 1: wbt_#1
Hint
where <wbt_tool> is /root/python_modules/super_pulsar/super_pulsar/tools/wbt_tool.py
Example 2
Merge two models named model1.joint, model2.joint into a model named model.joint, using the wbt_name that comes with the joint model
<wbt_tool> fuse --input model1.joint model2.joint --output model.joint
Attention
If wbt_tool info sees wbt_name as None for a joint model, you need to specify wbt_name manually, otherwise it will report an error when fuse.
Example 3
Split the model named model.joint into two models named model1.joint, model2.joint.
<wbt_tool> split --input model.joint --output model1.joint model2.joint
Example 4
Merge two models named model1.joint, model2.joint into a model named model.joint, and specify wbt_name in the model1.joint model as wbt1, wbt2, wbt_name in the model2.joint model as
.. code-block:: python
<wbt_tool> fuse –input model1.joint model2.joint –output model.joint –wbt_name wbt1 wbt2
Example 5
Split the model named model.joint, which has four wbt parameters with index``s of ``0, 1, 2, 3,
Take only the two wbt``s with ``index of 1, 3, package them as joint models, and name them model_idx1.joint, model_idx3.joint
<wbt_tool> split --input model.joint --output model_idx1.joint model_idx3.joint --indexes 1 3
Attention
If you have any questions about using it, please contact the relevant FAE student for support.
5.6. How to configure config prototxt in different scenarios
Hint
Pulsar can perform complex functions by properly configuring config, which is explained below for some common scenarios.
Note: The code examples provided in this section are code snippets that need to be manually added to the appropriate location by the user.
5.6.1. Search PTQ Model Mix Bit Configuration
Prior work
Ensure that the current onnx model and the configuration file config_origin.prototxt can be successfully converted to a joint model during pulsar build.
Copy and modify the configuration file
COPY the configuration file config_origin.prototxt and name it mixbit.prototxt, then make the following changes to mixbit.prototxt:
output_typeis specified asOUTPUT_TYPE_SUPERNETAdd
task_conftoneuwizard_confand add mixbit search-related configuration as needed
The config example is as follows:
1# Basic configuration parameters: Input and output
2...
3output_type: OUTPUT_TYPE_SUPERNET
4...
5
6# Configuration parameters for the neuwizard tool
7neuwizard_conf {
8 ...
9 task_conf{
10 task_strategy: TASK_STRATEGY_SUPERNET # 不可修改
11 supernet_options{
12 strategy: SUPERNET_STRATEGY_MIXBIT # 不可修改
13 mixbit_params{
14 target_w_bit: 8 # Set the average weight bit, supports fractional numbers but must be in the range of w_bit_choices
15 target_a_bit: 6 # Set average feature bit, supports fractional values but must be in the range of f_bit_choices
16 w_bit_choices: 8 # weight bits are currently only supported in [4, 8], due to prototxt limitations each option must be written in separate lines
17 a_bit_choices: 4 # feature # feature currently only supports [4, 8, 16], due to prototxt limitations you must write each option in a separate line
18 a_bit_choices: 8
19 # MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_HAWQv2, MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_MSE, MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_COS_SIM are currently supported,
20 # where hawqv2 is slower and may require a small calibration batchsize, MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_MSE is recommended
21 metric_type: MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_MSE
22 }
23 }
24 }
25 ...
26}
Attention
Current metric_type support configuration
MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_HAWQv2
MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_MSE
MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_COS_SIM
Among them, HAWQv2 is slower and may require a smaller calibration batchsize, MIXBIT_METRIC_TYPE_MSE is recommended.
Conduct a mixbit search
In the toolchain docker, execute the following command
1pulsar build --config mixbit.prototxt --input your.onnx # If the model path is already configured in config, you can omit --input xxx
The mixbit_operator_config.prototxt file and the onnx_op_bits.txt file will be generated in the current directory after compilation.
mixbit_operator_config.prototxtis a mixbit search result that can be used directly to configureprototxtonnx_op_bits.txtoutputs the inputfeatureandweight bitfor each weight layer in the.onnxmodel, as well as thesensitivitycalculated for eachbit(smaller values indicate less impact on model performance)
Attention
When searching mixbit, if the evaluation_conf field is configured in mixbit.prototxt, an error will be reported during the compilation process, but it will not affect the final output, so it can be ignored.
Add the mixbit search results to the configuration file and compile the model based on the mixbit configuration.
Copy everything from mixbit_operator_config.prototxt directly to config_origin.prototxt (without the mixbit-related configuration above) in the neuwizard_conf->operator_conf file, as shown in the example below:
1# Configuration parameters for the neuwizard tool
2neuwizard_conf {
3 ...
4 operator_conf{
5 ...
6 operator_conf_items {
7 selector {
8 op_name: "192"
9 }
10 attributes {
11 input_feature_type: UINT4
12 weight_type: INT8
13 }
14 }
15 operator_conf_items {
16 selector {
17 op_name: "195"
18 }
19 attributes {
20 input_feature_type: UINT8
21 weight_type: INT4
22 }
23 }
24 ...
25 }
26 ...
27}
Execute the following command in the toolchain docker:
1# The parameters of the command need to be configured according to the actual requirements, and are used here for illustrative purposes only
2pulsar build --config config_origin.prototxt --input your.onnx
The final compiled hybrid bit model is your.joint. The following tests show how the models behave when configuring different bits for Resnet18 and Mobilenetv2 respectively.
Resnet18
resnet18 |
Float top1 |
QPS |
search time |
|---|---|---|---|
float |
69.88% |
/ |
/ |
8w8f |
69.86% |
92.92 |
/ |
[mse or cos_sim] 6w8f |
68.58% |
135.39 |
4s |
hawqv2 6w8f |
68.58% |
135.39 |
3min |
[mse or cos_sim] 5w8f |
66.52% |
153.14 |
4s |
hawqv2 5w8f |
66.52% |
153.14 |
3min |
hawqv2 5w7f |
65.72% |
157.59 |
7min |
[mse or cos_sim] 5w7f |
65.8% |
157.35 |
8s |
4w8f |
55.66% |
169.35 |
/ |
Mobilenetv2
mobilenetv2 |
float top1 |
QPS |
search time |
|---|---|---|---|
float |
72.3% |
/ |
/ |
8w8f |
71.02% |
165.78 |
/ |
hawqv2 6w8f |
68.96% |
172.10 |
61min |
[mse or cos_sim] 6w8f |
69.2% |
173.33 |
6s |
[mse or cos_sim] 8w6f |
69.56% |
174.30 |
4s |
Note
The above tedious operation is essentially configuring the search results into config_origin.prototxt and compiling the joint model based on the search configuration.
5.6.2. Layer-by-layer pairs of sub
Attention
Note: The layer-by-layer pairing feature is only available in docker toolchains with version numbers greater than 0.6.1.2.
You need to add the following to the configuration file
dataset_conf_error_measurement {
path: "../dataset/imagenet-1k-images.tar"
type: DATASET_TYPE_TAR # The dataset type is tar package
size: 256 # The actual number of images used in the calibration quantification process
}
evaluation_conf {
path: "neuwizard.evaluator.error_measure_evaluator"
type: EVALUATION_TYPE_ERROR_MEASURE
source_ir_types: IR_TYPE_ONNX
ir_types: IR_TYPE_LAVA
score_compare_per_layer: true
}
The full example is as follows (using resnet18 config as an example)
# Basic configuration parameters: input and output
input_type: INPUT_TYPE_ONNX
output_type: OUTPUT_TYPE_JOINT
# Hardware platform selection
target_hardware: TARGET_HARDWARE_AX620
# CPU backend selection, default is AXE
cpu_backend_settings {
onnx_setting {
mode: DISABLED
}
axe_setting {
mode: ENABLED
axe_param {
optimize_slim_model: true
}
}
}
# Model input data type settings
src_input_tensors {
color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_RGB
}
dst_input_tensors {
color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_RGB
# color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_NV12 # If the input data is NV12, then this configuration is used
}
# Configuration parameters for the neuwizard tool
neuwizard_conf {
operator_conf {
input_conf_items {
attributes {
input_modifications {
affine_preprocess {
slope: 1
slope_divisor: 255
bias: 0
}
}
input_modifications {
input_normalization {
mean: [0.485,0.456,0.406] ## mean
std: [0.229,0.224,0.255] ## std
}
}
}
}
}
dataset_conf_calibration {
path: "... /dataset/imagenet-1k-images.tar" # Set the path to the PTQ calibration dataset
type: DATASET_TYPE_TAR # dataset type: tarball
size: 256 # Quantify the actual number of images used in the calibration process
batch_size: 1
}
dataset_conf_error_measurement {
path: "... /dataset/imagenet-1k-images.tar"
type: DATASET_TYPE_TAR # Dataset type: tarball
size: 4 # The actual number of images used in the layer-by-layer pairing process
}
evaluation_conf {
path: "neuwizard.evaluator.error_measure_evaluator"
type: EVALUATION_TYPE_ERROR_MEASURE
source_ir_types: IR_TYPE_ONNX
ir_types: IR_TYPE_LAVA
score_compare_per_layer: true
}
}
# Output layout settings, NHWC is recommended for faster speed
dst_output_tensors {
tensor_layout:NHWC
}
# Configuration parameters for pulsar compiler
pulsar_conf {
ax620_virtual_npu: AX620_VIRTUAL_NPU_MODE_111 # require to use ISP, must use the vNPU 111 configuration, 1.8Tops of arithmetic power to the user's algorithm model
batch_size: 1
debug : false
}
In the pulsar build process, the accuracy loss of each layer of the model is printed out, as shown in the figure below.
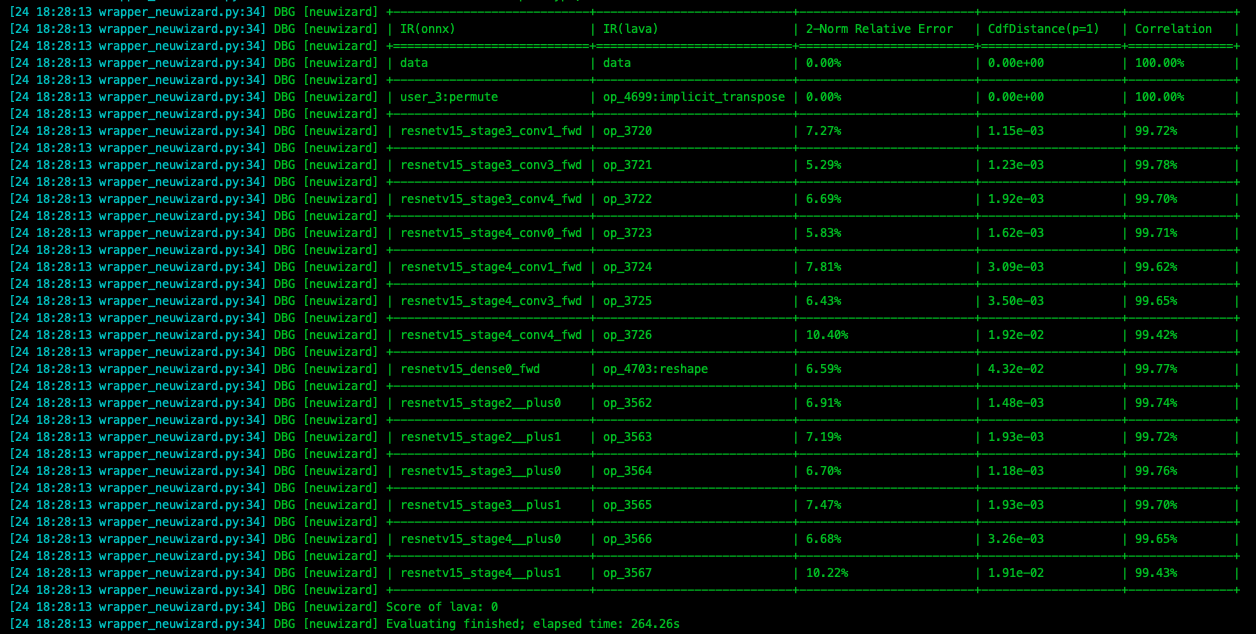
Warning
Note that adding this configuration will significantly increase the compilation time of the model.
5.6.3. Multiple inputs, different configurations for different channels CSC
CSC stands for Color Space Convert. The following configuration means that the data_0 input color space of the input model (i.e., the ONNX model) is BGR,
The input color space of data_0 of the compiled output model (i.e., the JOINT model) will be modified to NV12, as described in tensor_conf configuration.
In short, it is what the input tensor is for the pre-compiled model, and what the input tensor is for the post-compiled model.
Code example 1
1src_input_tensors {
2 tensor_name: "data_0"
3 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_BGR # The color space of the `data_0` road input used to describe or illustrate the model
4}
5dst_input_tensors {
6 tensor_name: "data_0"
7 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_NV12 # Color space of the `data_0` road input used to modify the output model
8}
where tensor_name is used to select a certain tensor. color_space is used to configure the color space of the current tensor.
Hint
The default value of color_space is TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_AUTO , which is automatically recognized based on the number of channels entered by the model, 3-channel for BGR;
1-channel is GRAY . So if the color space is BGR, src_input_tensors can be left out, but sometimes src_input_tensors and dst_input_tensors usually come in pairs to better describe the information.
Code Example 2
1src_input_tensors {
2 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_AUTO
3}
4dst_input_tensors {
5 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_AUTO
6}
The number of channels is automatically selected based on the input tensor, which can be omitted but is not recommended.
Code Example 3
1src_input_tensors {
2tensor_name: "data_0"
3 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_RGB # The color space of the original input model's `data_0` input is RGB
4}
5dst_input_tensors {
6 tensor_name: "data_0"
7 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_NV12
8 color_standard: CSS_ITU_BT601_STUDIO_SWING
9}
The above configuration means that the input color space of data_0 of the input model (i.e. ONNX model) is RGB, while the input color space of data_0 of the compiled output model (i.e. JOINT model) will be modified to NV12, and the color_standard will be configured as CSS_ITU_BT601_STUDIO_SWING .
5.6.4. cpu_lstm configuration
Hint
If there is an lstm structure in the model, you can configure it by referring to the following configuration file to ensure that the model will not have exceptions on this structure.
1operator_conf_items {
2 selector {}
3 attributes {
4 lstm_mode: LSTM_MODE_CPU
5 }
6}
A complete configuration file reference (containing cpu_lstm, rgb, nv12) example
1input_type: INPUT_TYPE_ONNX
2output_type: OUTPUT_TYPE_JOINT
3
4src_input_tensors {
5 tensor_name: "data"
6 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_RGB
7}
8dst_input_tensors {
9 tensor_name: "data"
10 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_NV12
11 color_standard: CSS_ITU_BT601_STUDIO_SWING
12}
13
14target_hardware: TARGET_HARDWARE_AX630 # You can override this configuration with command line arguments
15neuwizard_conf {
16 operator_conf {
17 input_conf_items {
18 attributes {
19 input_modifications {
20 input_normalization { # input data normalization, the order of mean/std is related to the color space of the input tensor
21 mean: 0
22 mean: 0
23 mean: 0
24 std: 255.0326
25 std: 255.0326
26 std: 255.0326
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
31 operator_conf_items { # lstm
32 selector {}
33 attributes {
34 lstm_mode: LSTM_MODE_CPU
35 }
36 }
37 }
38 dataset_conf_calibration {
39 path: "../imagenet-1k-images.tar"
40 type: DATASET_TYPE_TAR
41 size: 256
42 batch_size: 32
43 }
44}
45pulsar_conf {
46 batch_size: 1
47}
In the case of cpu_lstm only, the full configuration file is referenced below:
1input_type: INPUT_TYPE_ONNX
2output_type: OUTPUT_TYPE_JOINT
3input_tensors {
4 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_AUTO
5}
6output_tensors {
7 color_space: TENSOR_COLOR_SPACE_AUTO
8}
9target_hardware: TARGET_HARDWARE_AX630
10neuwizard_conf {
11 operator_conf {
12 input_conf_items {
13 attributes {
14 input_modifications {
15 affine_preprocess { # Affine the data, i.e. `* k + b`, to change the input data type of the compiled model
16 slope: 1 # Change the input data type from floating point [0, 1) to uint8
17 slope_divisor: 255
18 bias: 0
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 }
23 operator_conf_items {
24 selector {}
25 attributes {
26 lstm_mode: LSTM_MODE_CPU
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 dataset_conf_calibration {
31 path: "../imagenet-1k-images.tar"
32 type: DATASET_TYPE_TAR
33 size: 256
34 batch_size: 32
35 }
36}
37pulsar_conf {
38 batch_size: 1
39}
Hint
In attributes you can modify the data type directly, which is a forced type conversion, while affine in input_modifications converts floating-point data to UINT8 with a * k + b operation.
5.6.5. Dynamic Q values
Dynamic Q values are calculated automatically, and can be seen in the log message printed by run_joint.
Code example
1dst_output_tensors {
2 data_type: INT16
3}
5.6.6. Static Q values
The difference between dynamic Q values is the explicit configuration of quantization_value.
Code example
1dst_output_tensors {
2 data_type: INT16
3 quantization_value: 256
4}
For a detailed description of the Q value see QValue Introduction
5.6.7. FLOAT input configuration
If you expect the compiled joint model of onnx to have the FLOAT32 type as input when you go to the board,
you can configure prototxt according to the following example.
Code example
1operator_conf {
2 input_conf_items {
3 attributes {
4 type: FLOAT32 # Here it is agreed that the compiled model will have float32 as the input type
5 }
6 }
7}
5.6.8. Multiple inputs, different data types for different channels
If you expect a two-way onnx compiled joint model to be loaded with UINT8 as input and FLOAT32 as input,
See the following example prototxt configuration.
Code example
1operator_conf {
2 input_conf_items {
3 selector {
4 op_name: "input1"
5 }
6 attributes {
7 type: UINT8
8 }
9 }
10 input_conf_items {
11 selector {
12 op_name: "input2"
13 }
14 attributes {
15 type: FLOAT32
16 }
17 }
18}
5.6.9. 16bit quantization
Hint
Consider 16bit quantization when quantization accuracy is not sufficient.
Code example
1operator_conf_items {
2 selector {
3
4 }
5 attributes {
6 input_feature_type: UINT16
7 weight_type: INT8
8 }
9}
5.6.10. Joint Layout配置
Before toolchain axera/neuwizard:0.6.0.1, the output Layout of the toolchain compiled model varies depending on the situation and cannot be configured.
After 0.6.0.1, if the post-compile model output Layout is not configured in pulsar build or in the configuration options, the toolchain defaults to NCHW for the post-compile model output Layout.
Modify the joint output Layout via the configuration file as follows:
1dst_output_tensors {
2 tensor_layout: NHWC
3}
Explicit configuration: add the --output_tensor_layout nhwc option to the pulsar build compiler directive.
Hint
Since the default layout layout of NHWC is internal to the hardware, it is recommended to use NHWC to get higher FPS.
5.6.11. Multiplex Calibration dataset
The following configuration describes a two-way input model with different calibration datasets for each way, where input0.tar and input1.tar are the data sets associated with the training dataset, respectively.
1dataset_conf_calibration {
2 dataset_conf_items {
3 selector {
4 op_name: "0" # The tensor name of one input.
5 }
6 path: "input0.tar" # Calibration dataset used `input0.tar`
7 }
8 dataset_conf_items {
9 selector {
10 op_name: "1" # The tensor name of the other input.
11 }
12 path: "input1.tar" # Calibration dataset used `input1.tar`
13 }
14 type: DATASET_TYPE_TAR
15 size: 256
16}
5.6.12. Calibration dataset as non-image type
For detection and classification models, the training data is generally a dataset of UINT8 images,
For behavioral recognition models such as ST-GCN, the training data is generally a set of float type coordinate points.
Currently, the Pulsar toolchain supports the configuration of calibration for non-image sets, which is described in the next section.
… attention:
- The ``calibration`` dataset should have the same distribution as the training and test datasets
- ``calibration`` should be given as a ``tar`` file consisting of ``.bin`` if it is not an image
- ``.bin`` must be consistent with the ``shape`` and ``dtype`` of the ``onnx`` model input
Take ST-GCN as an example of how to configure calibration for a non-image set.
ST-GCN Dual Input Example
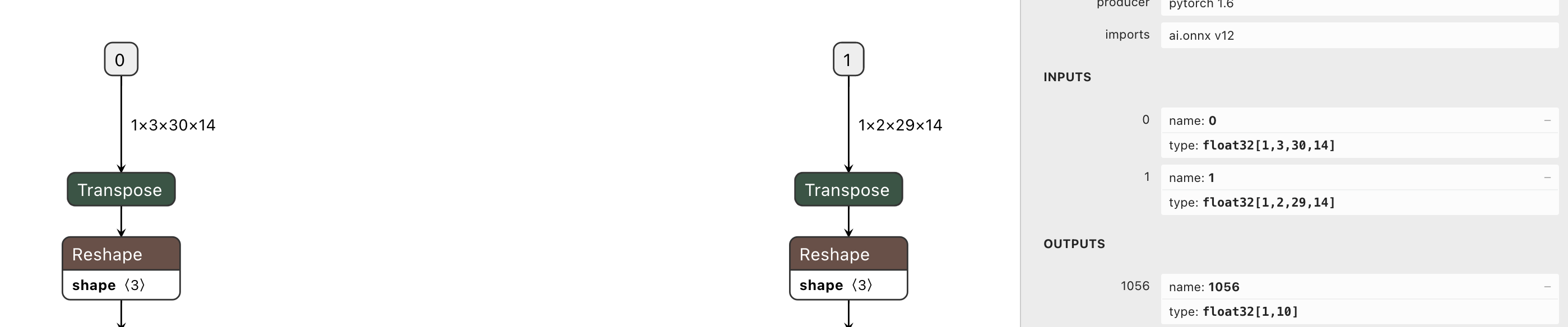
As you can see from the figure above:
The input
tensor_nameof the two-waySTGCNmodel is0and1respectively, and thedtypeisfloat32.Following the :ref:
multi_calibrations_inputconfiguration method, it is easy to configureconfigcorrectlyThe details of how to create the
tarfile will be explained later
Dual input without pairing
The .tar file for calibration is explained in the case of a model with two inputs that does not require pairing.
Reference Code
1import numpy as np
2import os
3import tarfile
4
5
6def makeTar(outputTarName, sourceDir):
7 # Create a tarball
8 with tarfile.open( outputTarName, "w" ) as tar:
9 tar.add(sourceDir, arcname=os.path.basename(sourceDir))
10
11input_nums = 2 # two-way input, e.g. stgcn
12case_nums = 100 # each tar contains 100 bin files
13
14# Create bin files with numpy
15for input_num in range(input_nums):
16 for num in range(case_nums):
17 if not os.path.exists(f "stgcn_tar_{input_num}"):
18 os.makedirs(f "stgcn_tar_{input_num}")
19 if input_num == 0:
20 # input shape and dtype must be consistent with the input tensor of the original model
21 # The input here is a random value, just as an example
22 # The specific training or test dataset should be read in the real application
23 input = np.random.rand(1, 3, 30, 14).astype(np.float32)
24 elif input_num == 1:
25 input = np.random.rand(1, 2, 29, 14).astype(np.float32)
26 else:
27 assert False
28 input.tofile(f"./stgcn_tar_{input_num}/cnt_input_{input_num}_{num}.bin")
29
30 # create tar file.
31 makeTar(f"stgcn_tar_{input_num}.tar", f"./stgcn_tar_{input_num}" )
Configure the path of the tar file generated by the above script to dataset_conf_calibration.dataset_conf_items.path in config,
dual inputs need to be paired
If dual inputs need to be paired, just make sure that the
.binfiles in bothtarhave the same nameFor example,
cnt_input_0_0.bin,cnt_input_0_1.bin, … instgcn_tar_0.tar. ,cnt_input_0_n.bin, and the files instgcn_tar_1.tarare namedcnt_input_1_0.bin,cnt_input_1_1.bin, … ,cnt_input_1_n.bin, the names of the files in the twotarare different, so it is not possible to pair the inputsIn short, when you need to pair inputs with each other, the file names of the paired inputs should be the same
Hint
- Note:
Setting
dtypeis not supported fortofile.If you want to read in a
binfile and restore the original data, you must specifydtype, and keep the samedtypeas intofile, otherwise you will get an error or a different number of elements.For example, if
dtypeisfloat64at the time oftofile, and the number of elements is1024, andfloat32at the time of reading, then the number of elements will change to2048, which is not as expected.
- Code example is as follows:
1input_0 = numpy.fromfile("./cnt_input_0_0.bin", dtype=np.float32) 2input_0_reshape = input_0.reshape(1, 3, 30, 14)
When the dtype of the fromfile operation is different from the tofile, the reshape operation will report an error.
When calibration is a float set, you need to specify the dtype of the input tensor in the config, which is UINT8 by default.
If this is not specified, a ZeroDivisionError may occur.
… attention:
For ``float`` inputs, note that the following is also required:
.. code-block:: python
:linenos:
operator_conf {
input_conf_items {
attributes {
type: FLOAT32
}
}
}
5.6.13. Configuration dynamics batch
After setting dynamic batch, it supports any batch_size of not exceeding the maximum value during inference, which is more flexible to use:
1pulsar_conf {
2 batch_size_option: BSO_DYNAMIC # Make the compiled model support dynamic batch
3 batch_size: 1
4 batch_size: 2
5 batch_size: 4 # Maximum batch_size is 4, requiring high performance for inference with batch_size of 1 2 or 4
6}
5.6.14. Configure static batch
Compared to :ref:dynamic_batch_size <dynamic_batch_size>, static batch is simpler to configure, as follows:
1pulsar_conf {
2 batch_size: 8 # batch_size can be 8 or other value
3}